Unveiling the Power of X-Ray Machines: A Visual Journey into Medical Imaging
Related Articles: Unveiling the Power of X-Ray Machines: A Visual Journey into Medical Imaging
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Power of X-Ray Machines: A Visual Journey into Medical Imaging. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Power of X-Ray Machines: A Visual Journey into Medical Imaging

The image of an X-ray machine, with its characteristically large, boxy form and intricate array of tubes and wires, holds a powerful significance in the realm of medical imaging. This seemingly simple apparatus, a cornerstone of modern healthcare, allows medical professionals to peer inside the human body, revealing hidden structures and pathologies that would otherwise remain invisible.
This article delves into the intricacies of X-ray machines, exploring their underlying principles, diverse applications, and the profound impact they have on patient care.
A Glimpse into the Inner Workings
X-ray machines harness the power of electromagnetic radiation, specifically a type known as X-rays, to create images of the body’s internal structures. These rays, invisible to the naked eye, have the unique ability to penetrate various materials, including soft tissues, bones, and even metals.
The process begins with the generation of X-rays within the machine’s X-ray tube. This tube, a crucial component of the device, contains a cathode and an anode. The cathode emits electrons, which are accelerated towards the anode by a high voltage. Upon striking the anode, these electrons produce X-rays, a form of high-energy radiation.
The X-rays then pass through the patient’s body, interacting with the tissues they encounter. Different tissues absorb X-rays to varying degrees, depending on their density. Dense materials, such as bones, absorb more X-rays than less dense materials, like soft tissues.
This differential absorption creates a pattern of shadows on an imaging plate or a digital detector placed behind the patient. The image, known as an X-ray radiograph, reveals the internal structures of the body, highlighting areas of high density (appearing white) and low density (appearing black).
Applications Spanning the Medical Spectrum
The versatility of X-ray technology is evident in its diverse applications across various medical specialties. From diagnosing fractures and identifying infections to evaluating the health of organs and guiding surgical procedures, X-ray machines play a critical role in patient care.
1. Diagnostic Imaging:
- Fractures and Dislocations: X-rays are indispensable for diagnosing bone fractures, sprains, and dislocations. The images clearly show the alignment of bones, revealing any breaks or misalignments.
- Pneumonia and Other Lung Conditions: X-rays provide valuable insights into the lungs, allowing doctors to detect pneumonia, lung infections, and other respiratory conditions.
- Dental Examinations: Dental X-rays are routinely used to assess the health of teeth, identify cavities, and evaluate the condition of bone surrounding the teeth.
- Abdominal Imaging: X-rays can help visualize the abdominal organs, aiding in the diagnosis of conditions like bowel obstructions, kidney stones, and appendicitis.
2. Guiding Medical Procedures:
- Fluoroscopy: This technique utilizes real-time X-ray imaging to guide procedures such as angiograms, where a contrast dye is injected into blood vessels to visualize their structure and identify blockages.
- Interventional Radiology: X-ray guidance allows for precise placement of catheters, stents, and other medical devices during minimally invasive procedures.
3. Radiation Therapy:
- Cancer Treatment: X-ray radiation can be used to target and destroy cancerous cells, playing a crucial role in the treatment of various cancers.
Beyond the Conventional: Advancements in X-Ray Technology
The field of X-ray technology is constantly evolving, with advancements leading to more precise, efficient, and patient-friendly imaging techniques.
1. Digital Radiography (DR): Replacing traditional film-based X-rays, digital radiography utilizes digital detectors to capture X-ray images directly, eliminating the need for film processing. This offers numerous advantages, including faster image acquisition, improved image quality, and enhanced image manipulation capabilities.
2. Computed Tomography (CT) Scans: CT scans employ a sophisticated system of X-ray detectors that rotate around the patient, capturing multiple images from different angles. These images are then processed by a computer to create detailed cross-sectional views of the body, providing a comprehensive understanding of internal structures.
3. Cone-Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT): This technology offers a smaller, more focused X-ray beam compared to conventional CT, resulting in lower radiation exposure for the patient. CBCT is particularly useful for dental imaging, guiding dental implants, and assessing bone density.
4. Dual-Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry (DEXA): DEXA scans are specifically designed to measure bone density, playing a crucial role in diagnosing osteoporosis and monitoring bone health.
Addressing Common Questions
1. Is X-ray exposure harmful?
While X-rays are a form of ionizing radiation, the amount of exposure during a medical X-ray is typically low and considered safe. However, it is essential for medical professionals to minimize radiation exposure by utilizing appropriate techniques and shielding.
2. Are there alternatives to X-rays?
Yes, depending on the specific condition being investigated, alternative imaging modalities like ultrasound, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and positron emission tomography (PET) scans may be considered.
3. How can I prepare for an X-ray?
Preparation for an X-ray typically involves removing any metal objects, such as jewelry or eyeglasses, that could interfere with the image. In some cases, you may be asked to fast for a specific period before the exam.
4. What are the risks associated with X-rays?
The risks associated with X-rays are generally low, but they include the potential for radiation exposure, which can increase the risk of cancer in the long term. However, the benefits of X-ray imaging often outweigh these risks, especially when used for diagnosing and treating serious conditions.
Tips for Understanding X-Ray Images
- Examine the image carefully: Pay attention to the overall shape, size, and position of the structures depicted.
- Look for abnormalities: Identify any areas of increased or decreased density, unusual shadows, or distortions.
- Consider the patient’s history and symptoms: The X-ray image should be interpreted in conjunction with the patient’s medical history and presenting symptoms.
- Consult with a medical professional: If you have any questions or concerns about an X-ray image, consult with a doctor or other qualified healthcare provider.
Conclusion
The X-ray machine, a seemingly simple yet remarkable device, has revolutionized medical imaging, providing invaluable insights into the human body. Its ability to visualize internal structures, diagnose diseases, and guide medical procedures has significantly advanced patient care, making it a cornerstone of modern healthcare. As technology continues to evolve, X-ray imaging will continue to play a vital role in ensuring accurate diagnoses, effective treatments, and improved patient outcomes.
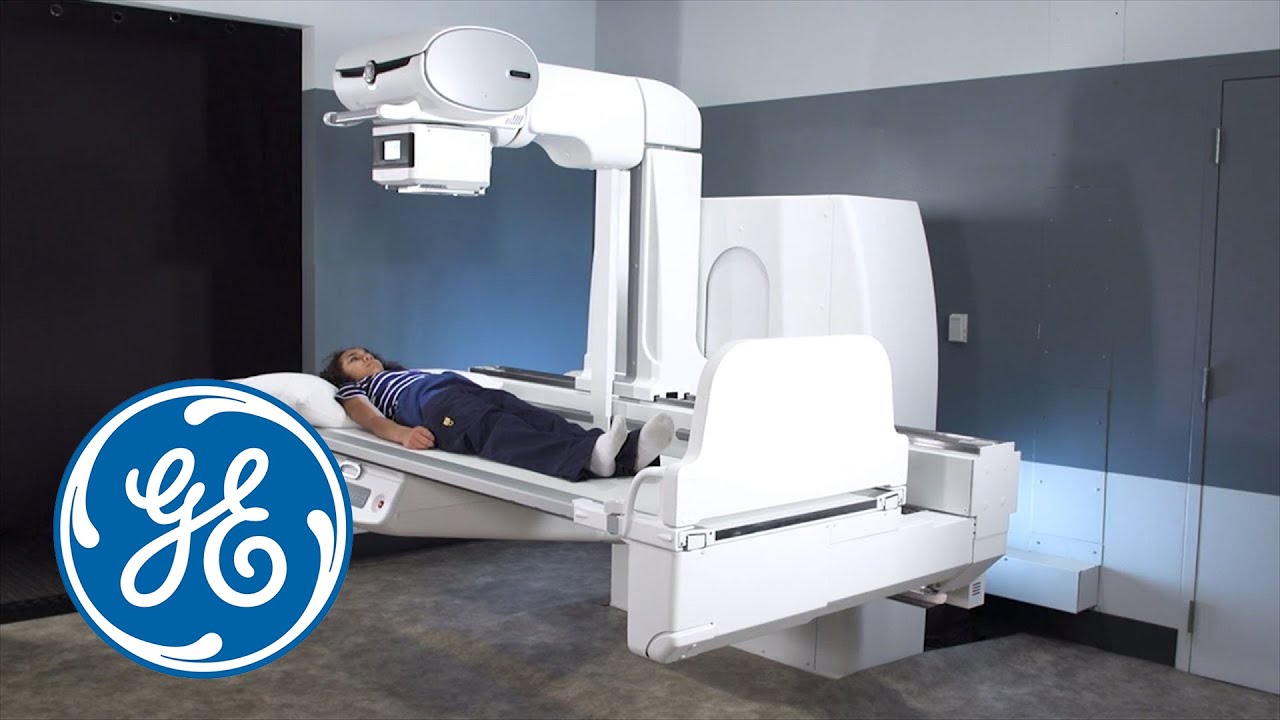



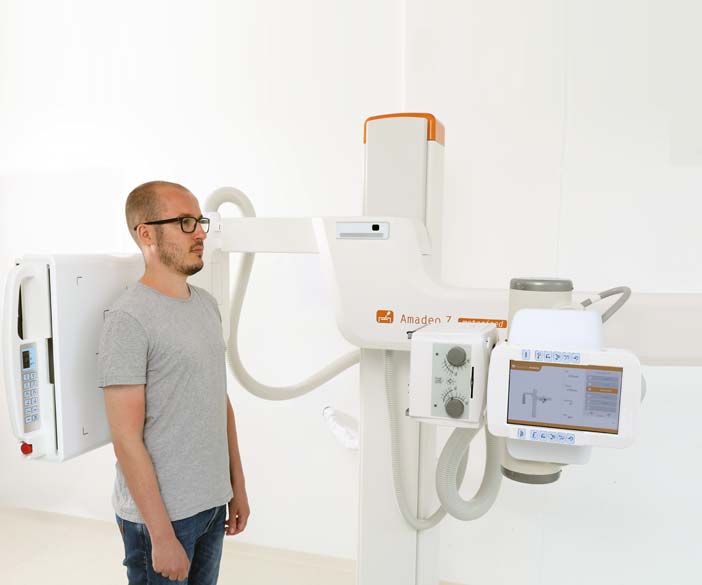
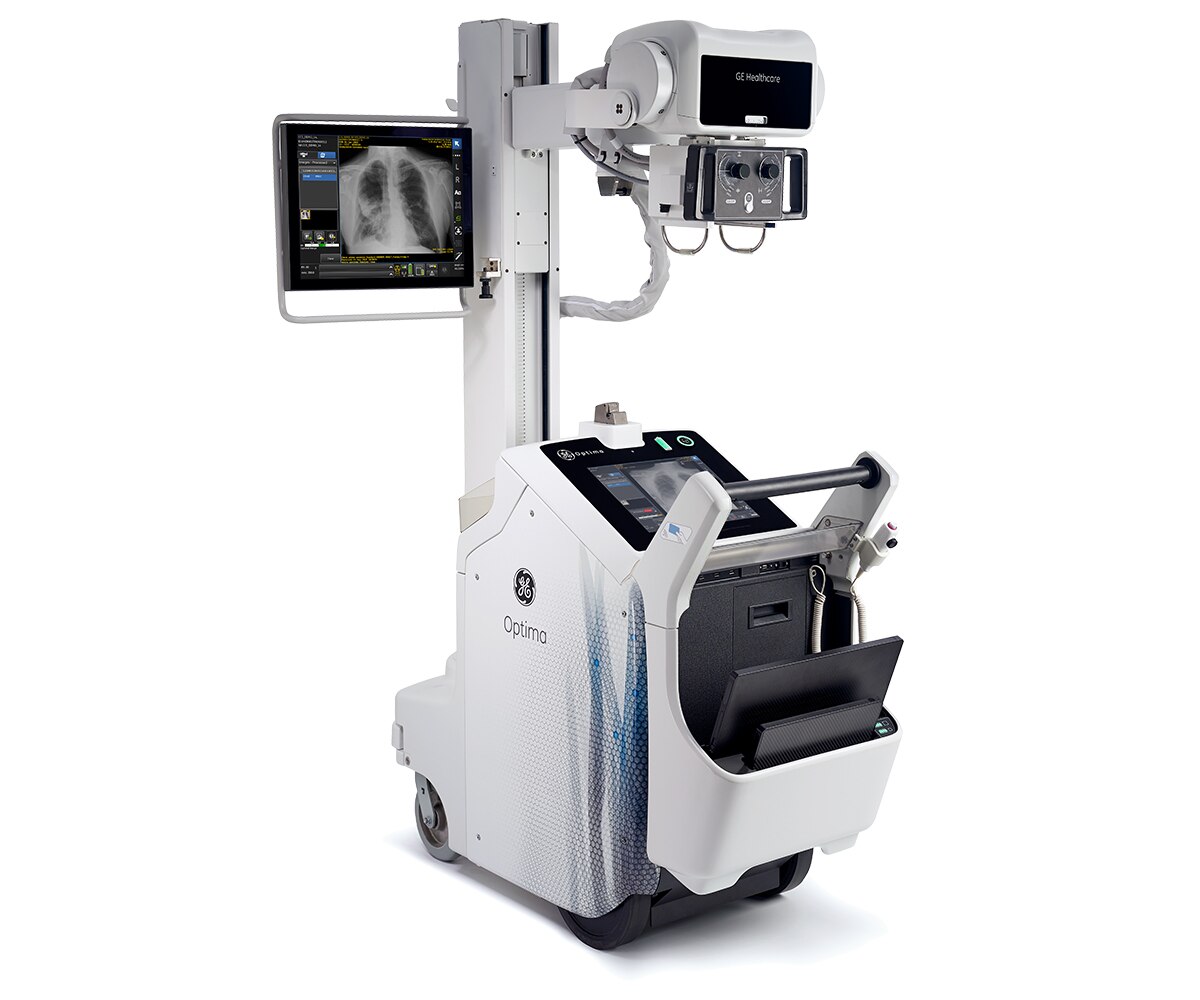


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Power of X-Ray Machines: A Visual Journey into Medical Imaging. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!